December 03, 2014
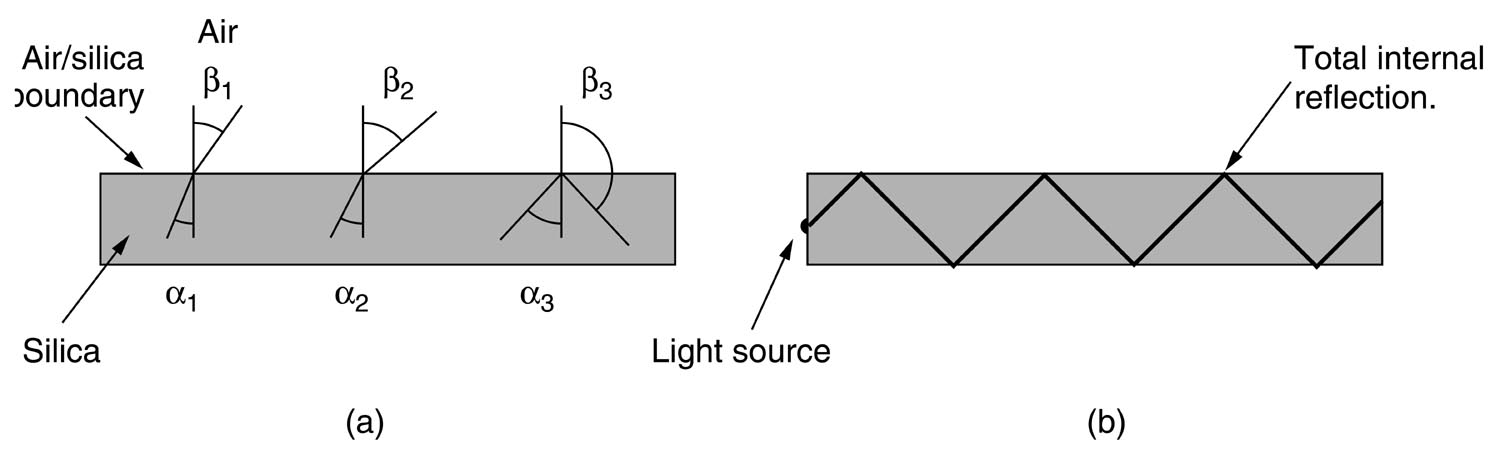
Figure 1.4 shows the principle of light propagation through a fiber optic cable. To understand the principle, consider when light is injected into an optical material that is surrounded by another optical material with a differnt index of refraction. The first and second optical materials will have a higher and lower index of refraction. The first and second optical materials will have a higher and lower index of refraction, respectively. Figure 1.4(a) shows light incident at an angleθto the normal. The light refracts by an angle βfrom the normal. If the angle of incidence is increased, the angle of refraction will also increase, as shown in Figure 1.4 (b). In Figure 1.4(c), light incident at an angleθequal to the critical angleθ gives an angle of refraction βof 90 degrees. The refracted light lies on the interface of the first-second optical materials. Snell’s Law is applicalbe here. In Figure 1.4(d), when light lands incident at an angle θ greater than the critical angle, the light will reflect by the total internal reflection phenomena. In this case, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, which is defined by the first law of light.
Assume the first optical material is very long. It has a circular cross section with a very small diameter like the core, and at the same time is surrounded by another optical material resembling the cladding in a fiber optic cable, as shown in Figure 1.4(e). Now, light injected into a fiber optic cable and striking the core-to-cladding interface at a greater angle than the critical angle reflects back into the core. Since the angles of incidence and reflection are equal, the relected light will again be reflected. The light will continueto bounce through the length of the fiber cable. Light in Figure 1.4 Cases (a), (b), and (c) show that the light passes into the cladding. The cladding is usually inefficient as a light carrier compared to the core of Plastic Optical Fiber Cable. Light in the cladding becomes part of the losses, some of which will be presented in coming sections of the chapter, that usually occur in any fiber optic cable. Therefore, light propagation in a fiber optic cable is governed by the following:
â— The wavelength of light
â— The angle of incidence of the light at the input of the fiber cable
â— The indices of refraction of the core and cladding
â— The composition of the core and cladding
â— The length of the cable
â— The bending radius of the cable
â— The sizes of the core and cladding
â— The design of the core and cladding
â— The transmission modes
â— The temperature and environment conditions of the fiber cable
â— The strength and flexibility of the fiber cable
Fiberstore provides affordable high quality cables and accessories to our customers, primarily focusing on the needs of the Fiber optic networks installers, and resellers of fiber optic products. All products can be custom fiber optic manufactured and guaranteed. Our fiber optic cable products have high degree of flexibility and customization. Buy Bulk Fiber Optic Cable from us, we can ensure you receive a product designed for your specific need and application, from straightforward simplex patch cords to custom optical sub-assemblies. We also provide fiber optic solution for customer, provide various and one-step fiber optic solutions to carriers and end-users with in-depth knowledge and overall consideration.
Posted by: kelonlau at
06:18 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 571 words, total size 5 kb.
33 queries taking 0.2613 seconds, 60 records returned.
Powered by Minx 1.1.6c-pink.